USA, Germany: While Knorr-Bremse has just entered the transport telematics market, announcing the equipment of its products with technical condition monitoring sensors, Wabtec and Trinity Rail continued to introduce new telematic platforms. Solutions are aimed at increasing the value of companies’ offers to customers.
Thus, Knorr-Bremse, one of the world’s largest manufacturers of components for rail transport, intends to equip the entire line of its products with telematics sensors, including brake systems, doors, air conditioning systems, etc. For this purpose, the company acquires a stake in the sensor producer, Nexxiot, and plans to invest €60 mln in its development. The purchase of a minority stake is announced, but allowing to influence strategic decisions. The transaction must be completed after the approval of the antimonopoly authorities.
The installed sensors should transmit data from the components to the Nexxiot digital ecosystem, which in turn will monitor the technical condition in real time and predict the date of the next repair, thereby reducing the cost of the product lifecycle. The subscription to the Nexxiot ecosystem is planned to be included in future Knorr-Bremse contracts with customers. The company expects that by 2027 revenues from this segment will amount to €200 mln.
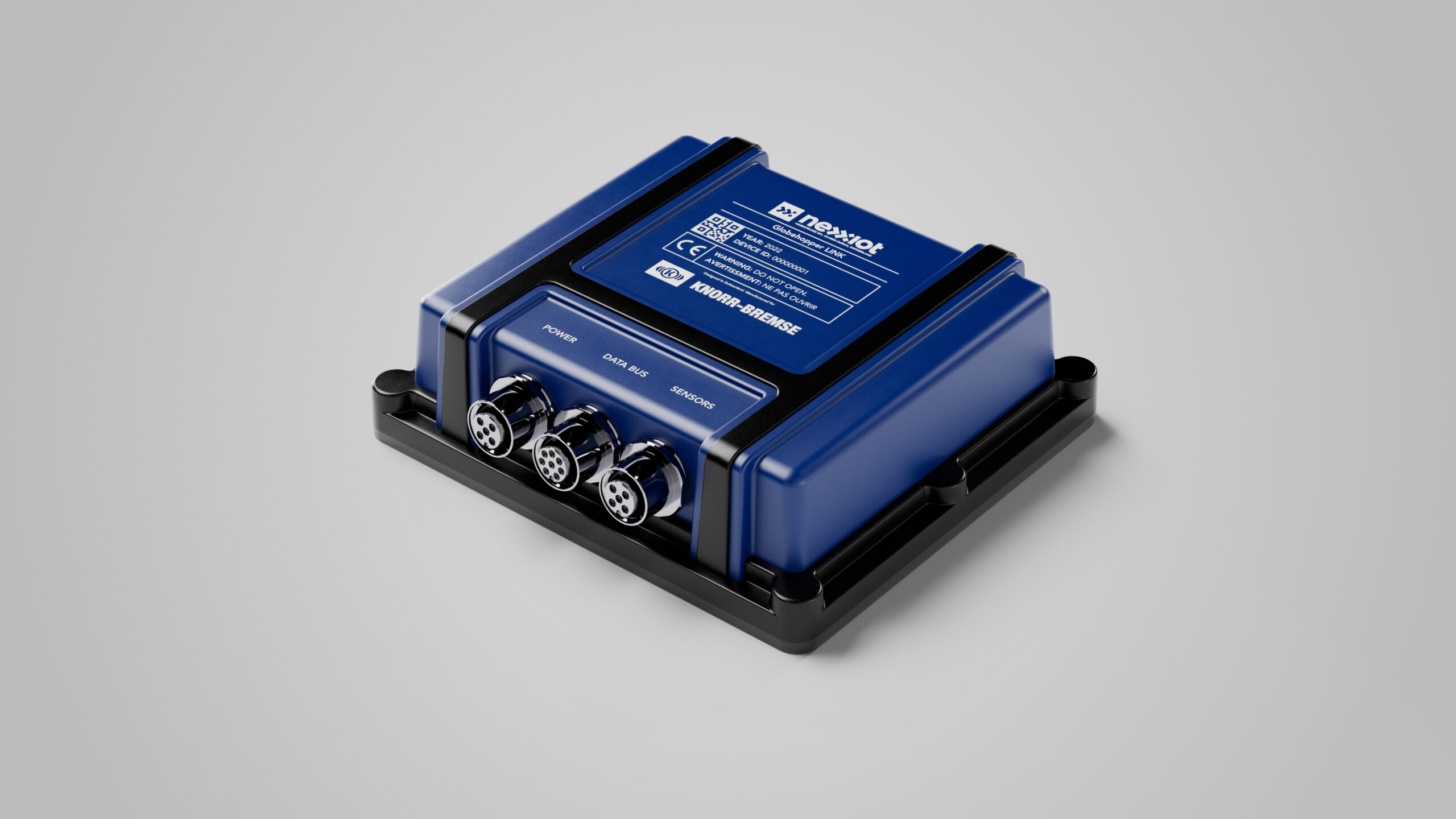 Nexxiot Globehopper LINK technical condition sensor based on IoT technologies. Source: Nexxiot
Nexxiot Globehopper LINK technical condition sensor based on IoT technologies. Source: Nexxiot
Nexxiot telematics sensors are already widely used in Europe on freight cars. According to the company, about 200,000 freight cars are equipped with it, which is more than 25% of the European operators’ fleet. The company intends to equip more than 2 mln railcars and containers worldwide with such devices by 2024.
Also, last week, Wabtec has launched the Precision Dispatch System platform, developed by order of Canadian National (CN). The platform processes data coming from sensors installed on rolling stock and railway infrastructure facilities, with the help of which it determines the location of railcars, their technical condition and malfunctions. The company says that the implementation of the platform on the CN network is expected at the end of next year.
Earlier in April, Wabtec acquired the Buena Vision division from Trimble, which manufactures equipment for monitoring the rolling stock technical condition based on computer vision technology. Buena Vision sensors and cameras allow to assess the condition of the rolling stock running gear components and the condition of the train itself during operation. Wabtec states that Buena Vision devices will be combined with TrackIQ system developed by the company itself, performing rolling stock inspection using a variety of sensors.
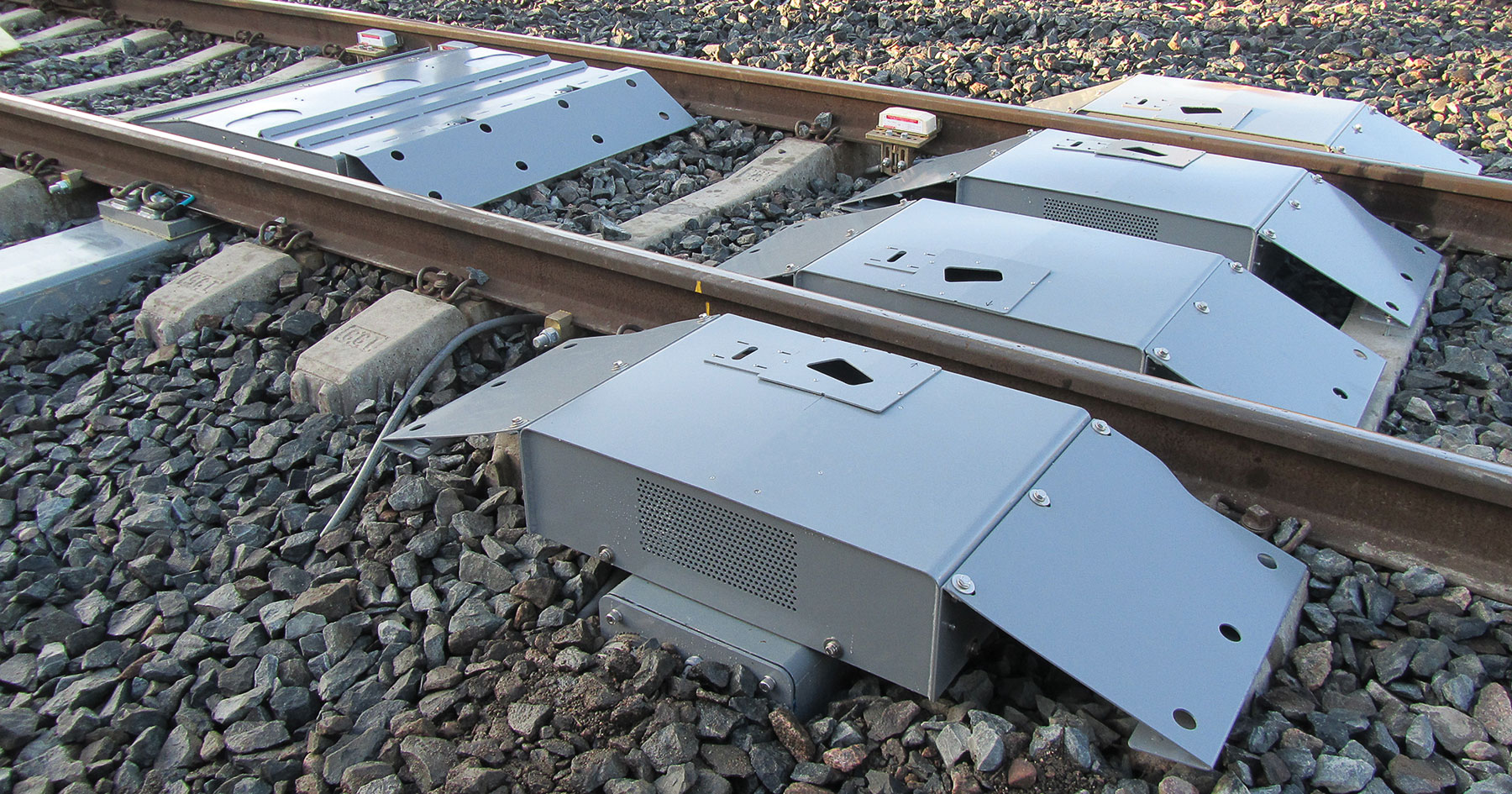 Buena Vision outdoor rolling stock monitoring systems (view). Source: Wabtec
Buena Vision outdoor rolling stock monitoring systems (view). Source: Wabtec
Additionally, Trinity Rail continued to expand its telematics asset portfolio by completing the acquisition of the Quasar (Quick Analytics for Shipping and Rail) platform from Cando Rail & Terminals to track the location of wagons in real time. This platform was launched in 2017 and $250 thsd USD was invested in its creation. The developers aimed to create a digital solution for the supply chain end-to-end control. The Quasar platform collects data from GPS sensors installed on railcars into a single database. Customers can monitor the movement of railcars online, the system determines their geolocation within half a meter.
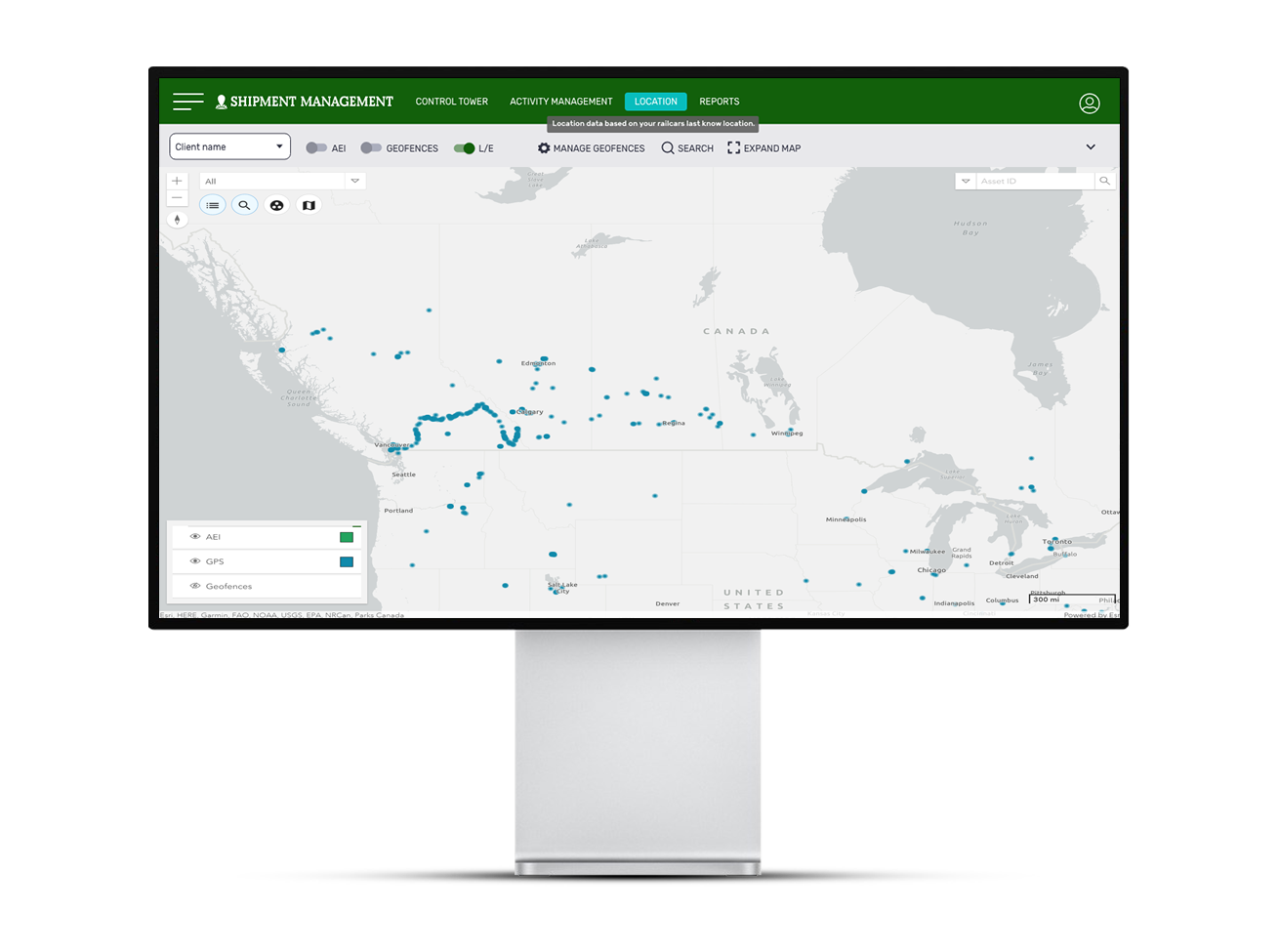 Quasar database screenshots. Source: quasarplatform.com
Quasar database screenshots. Source: quasarplatform.com
Last year, Trinity Rail launched its own Trinsight platform to track the location of freight cars, their technical condition, as well as a number of other indicators in real time. It was stated that the platform should process data from 132,000 cars owned and operated by Trinity Rail in North America (the car builder has its own leasing division). It was planned to integrate machine learning into the system for predictive analytics. The project is being implemented as part of the RailPulse project, a joint venture between Trinity Rail, GATX, Norfolk Southern and Genesee & Wyoming, aimed at expanding the use of telemetry in US freight transportation and partially supported by a $7.9 mln USD grant from the US Department of Transport.















