Russia: The Demikhovo Engineering Works (DMZ, part of TMH since 2005) launched the mass production of electric trains in Russia a little over 30 years ago, in 1992. Today, the DMZ products in the local fleet make 60% of such rolling stock. The 11,000th EMU car was produced at the factory in June this year. Now the plant is making towards the complete domestic production. For example, in the recently developed EP2DM electric train, the share of Russian components has been brought up to 99%. Also, a country’s strategically important project of mastering the production of reduction drives is being implemented at DMZ.
The development of EMUs production in Russia
Riga Car Building plant (RVR) was manufacturing electric trains for the 1,520 mm gauge area since the middle of the XX century, but after the USSR collapsed, it emerged abroad Russia. The Russian government decided to balance the disadvantage by repurposing DMZ, located close to Moscow. Previously, the plant produced freight and narrow-gauge cars.
The first ED2T electric train by DMZ was produced in 1993–1999. It was built on the basis of RVR technologies. The train was built for 3,000 V DC lines, had a design speed of 130 km/h, starting acceleration rate of 0.67 m/s2 and consisted of 4, 6 or 8-11 cars. Electrical equipment was supplied by Riga Electrical Equipment plant (RER).
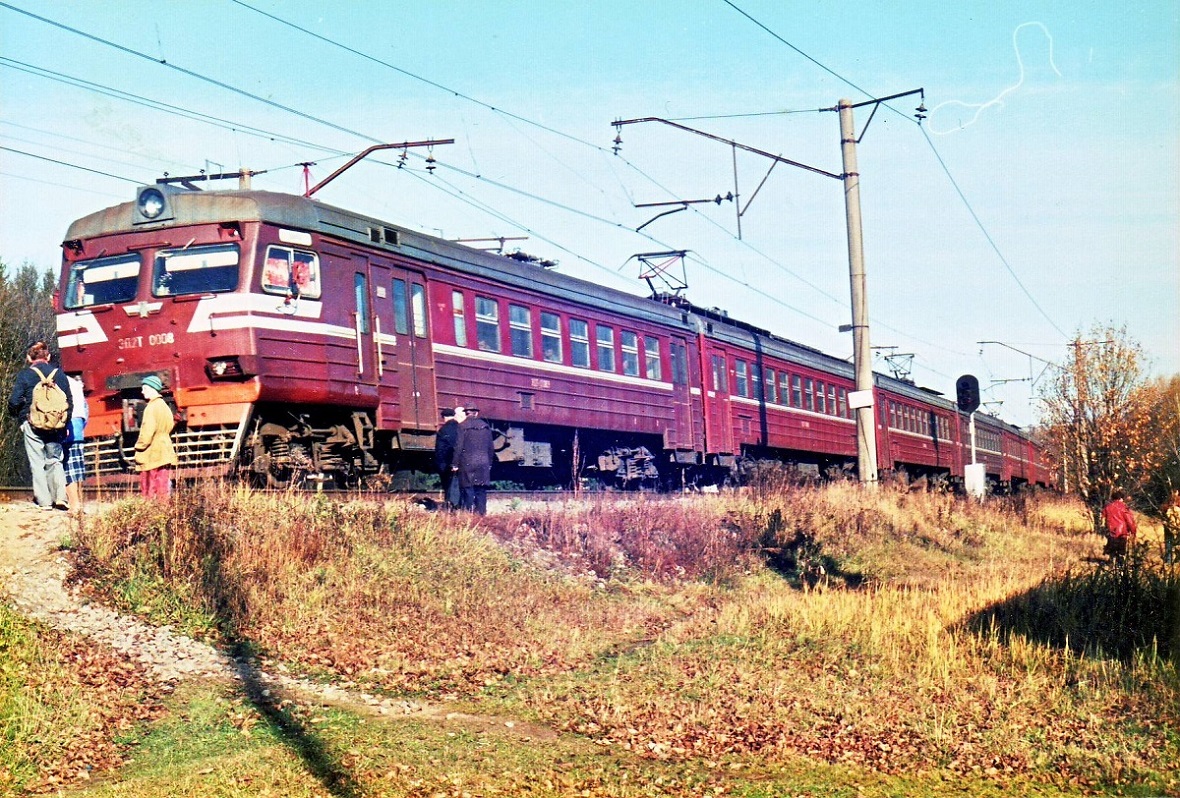 ED2T electric train. Source: V.V. Vinogradov/trainpix
ED2T electric train. Source: V.V. Vinogradov/trainpix
DMZ started to use Russian-made electrical equipment in the next platform of DC trains – ED4. Its production began in 1996 and continued for 20 years. At the same time, a significant part of trains was still equipped with electric components from Riga, Latvia. The series was updated regularly. One of the EMU modifications was ED4M and it became the most mass-produced in Russia with 4548 cars manufactured. The new trains were equipped with high-power auxiliary converters, external sliding plug doors, a microclimate system for compartments, sealed inter-car gangways, gapless inter-car coupling devices, the system of video surveillance inside cars.
Since 2016, DMZ has started serial production of the EP2D DC train. It was improved in terms of comfort and design: there were passenger compartments for economy and business classes. The train received from the ED4 a commutator type of motor and a control system along with an acceleration rate of 0.7 m/s2. The design speed of EP2D is 120 km/h. The train also has a set of electrical equipment powered by 1,500 V traction motors, static auxiliary converters, an aerodynamic driver’s cab of fiberglass, plain carriage sidewalls and roof slopes, asymmetric pantographs on the motor cars, batteries with a capacity of 120 Ah, air disinfection systems in the cars. A new technical feature was the possibility to form 2- and 3-car trains with a max composition of 12 cars. The request for such trains was previously announced by Russian Railways (RZD) in order to increase the efficiency of regional transportation on routes with low ridership.
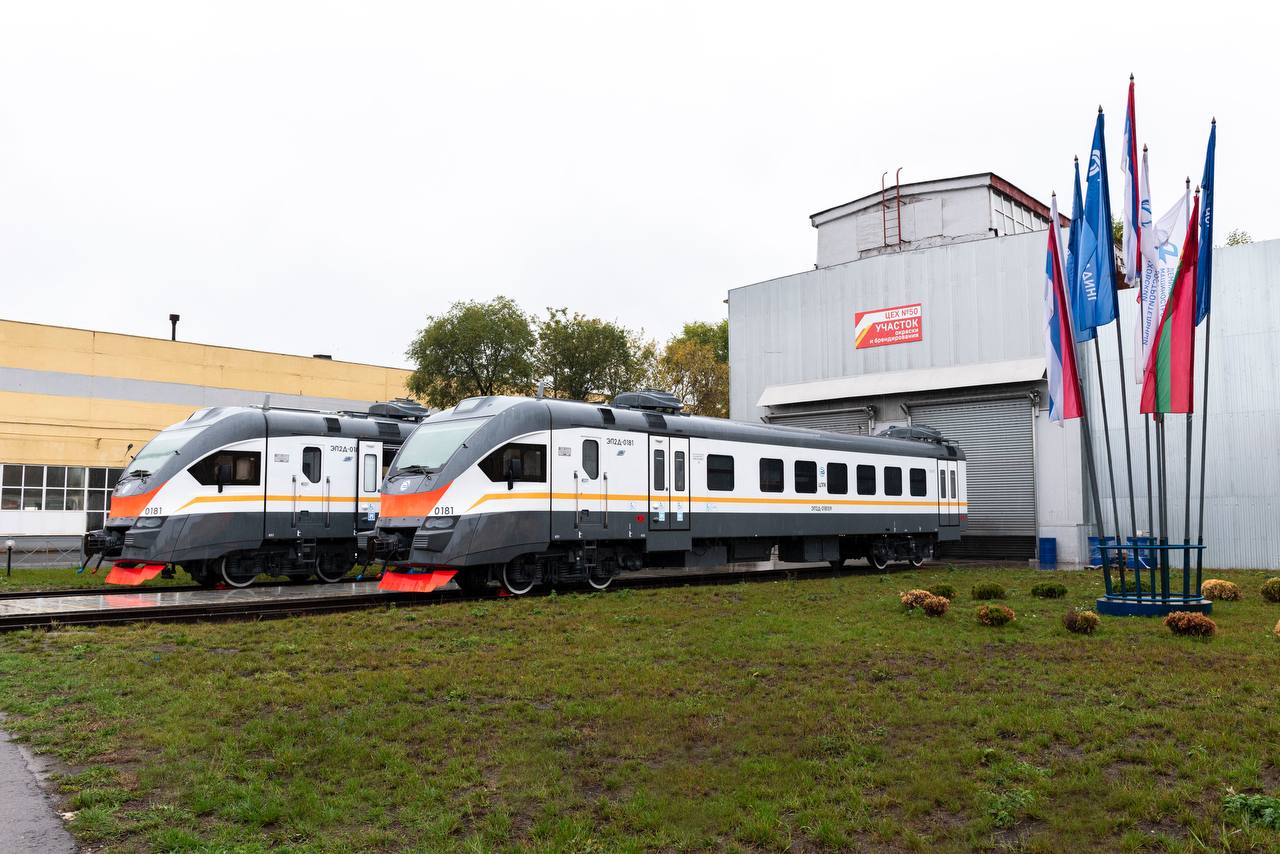 EP2D head cars. Source: DMZ
EP2D head cars. Source: DMZ
Nowadays, more than 2,000 EP2D cars have been produced, as well as 382 cars of the EP3D model for AC lines developed on its basis. The share of the locally produced components in EP2D is 90%, and in EP3D it was increased to 99%. If required by the operator, both trains can be adopted for operation on routes with high and low platforms. Today, EP2D and EP3D trains are in operation at 13 of 16 parts of RZD’s network and several batches of it were exported to Armenia and Kazakhstan.
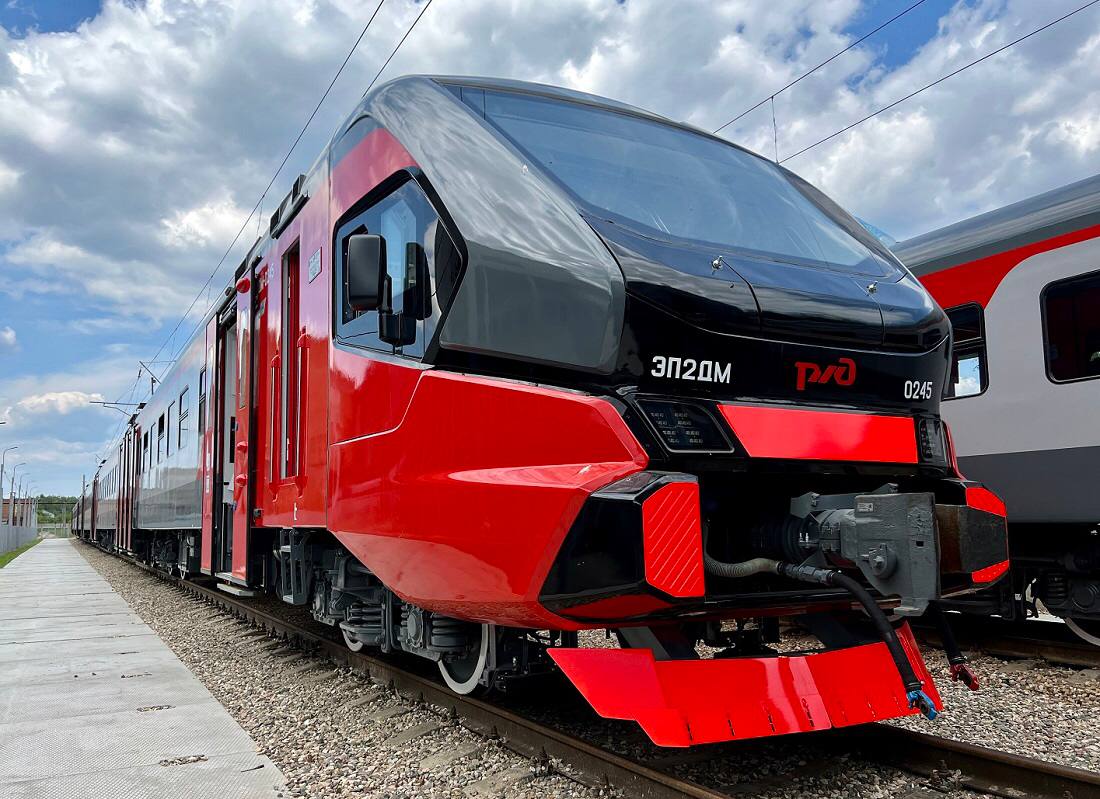
EP2DM train: as Russian as possible
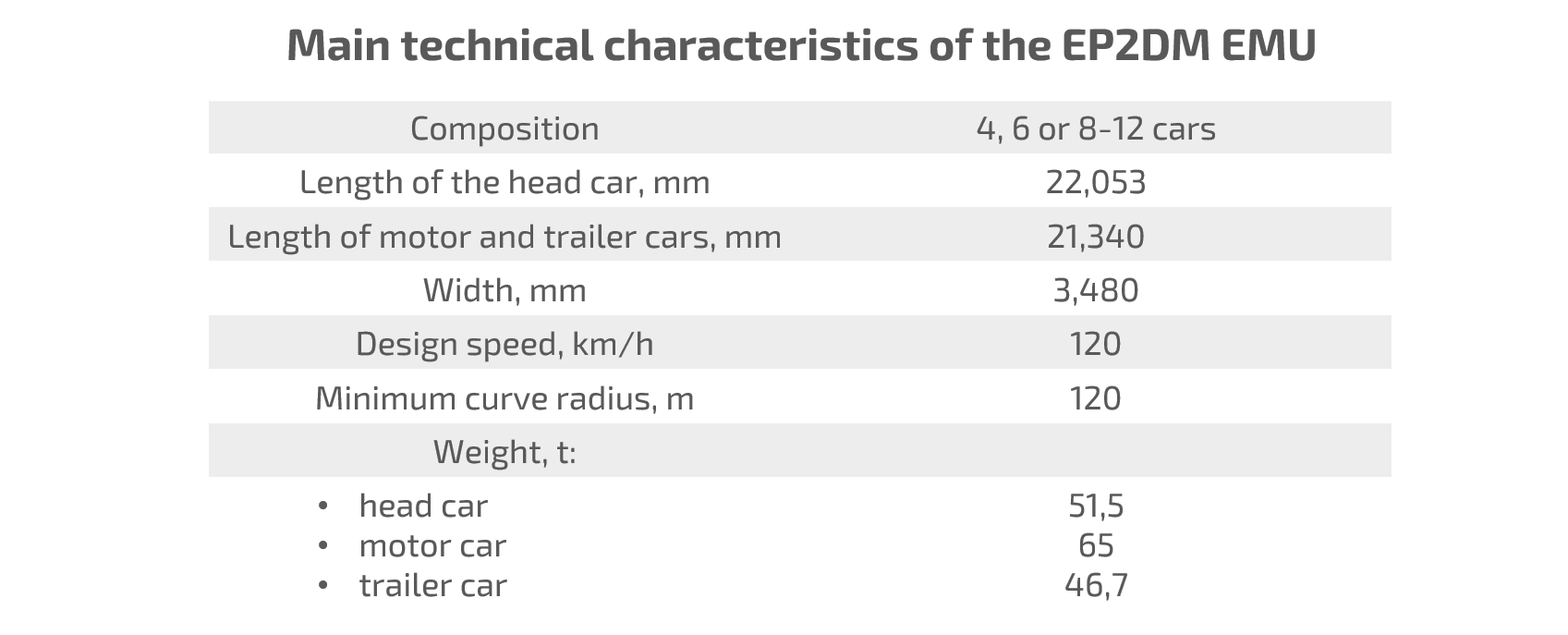
In 2022, a critical change in the geopolitical situation and the sanctions introduction on the supply of EU components showed the strategic importance of achieving real independence in local production, including rolling stock. By the beginning of this year, DMZ completed the assembly of the first EP2DM DC electric train with the max share of Russian components. More than 80 local enterprises took part in its creation. The first train passed approval trials at VNIIZHT Test Loop in Shcherbinka, and at the end of June received a certificate of conformity with the requirements of TR EAEU 001/2011. It is planned to produce 186 cars of this model in 2023.
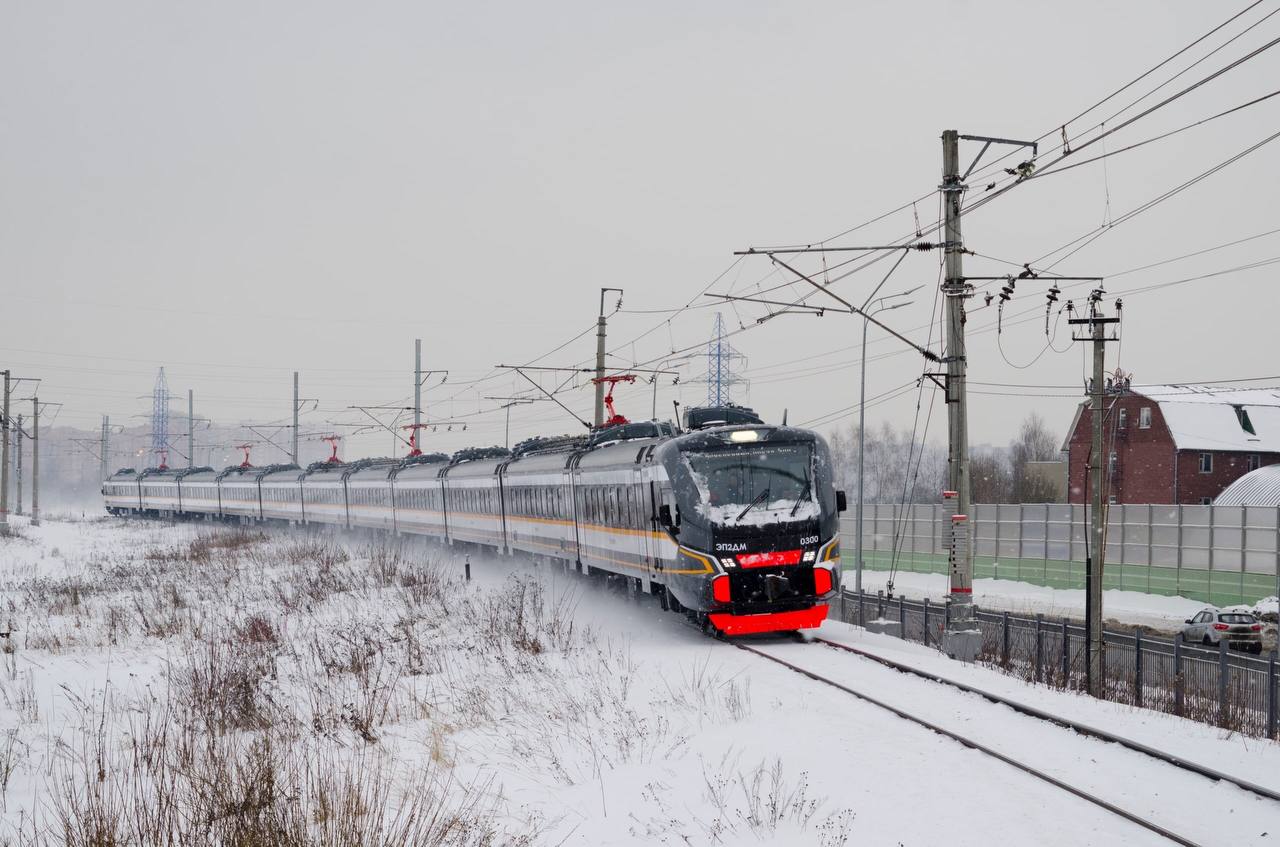 EP2DM electric train on trials. Source: Dmitry Bykovskiy
EP2DM electric train on trials. Source: Dmitry Bykovskiy
In EP2DM, a set of KEO-750 electrical equipment was used instead of KEO-1500 produced by RER. Also, the production of such components as traction motors and inter-car electrical connectors (also previously produced at RER), automatic and toggle switches was localized in Russia. The production of these parts was launched at the facilities of the Key Systems and Components Group, Sibelektroprivod, Tatelektromash and Kursk Electrical Equipment Plant. As noted earlier, the use of the Russian components made it possible to increase the level of train localization to 99%.
The non-localized 1% included, for example, clip connectors purchased in China. Also, the dependence on import still remains for components of the control panel, the main pneumatic compressor of the brake system, the details of HVAC system. The localization of the listed parts of the EP2DM train is planned to be completed during 2023.
The vehicle got a significant update in its design as well. It was developed together with the National Center for Industrial Design and Innovation 2050.LAB led by the core division of TMH Engineering incorporating the feedback from passengers and potential customers. EP2DM received a new look made in accordance with the TMH brand DNA. Changes in the body structure mainly referred to the shape of the frontal part of the cab. In comparison with EP2D, it had a concave bend at the level between the coupler and the windshield. The glass became wider, and the headlights were narrowed and received diagonal bevel angels. The shape of the cab eliminates train hopping. The coating of the livery has anti-vandal properties. The side windows of the cab have increased clear openings, which improves the possibility of evacuating the driver in case of an emergency.
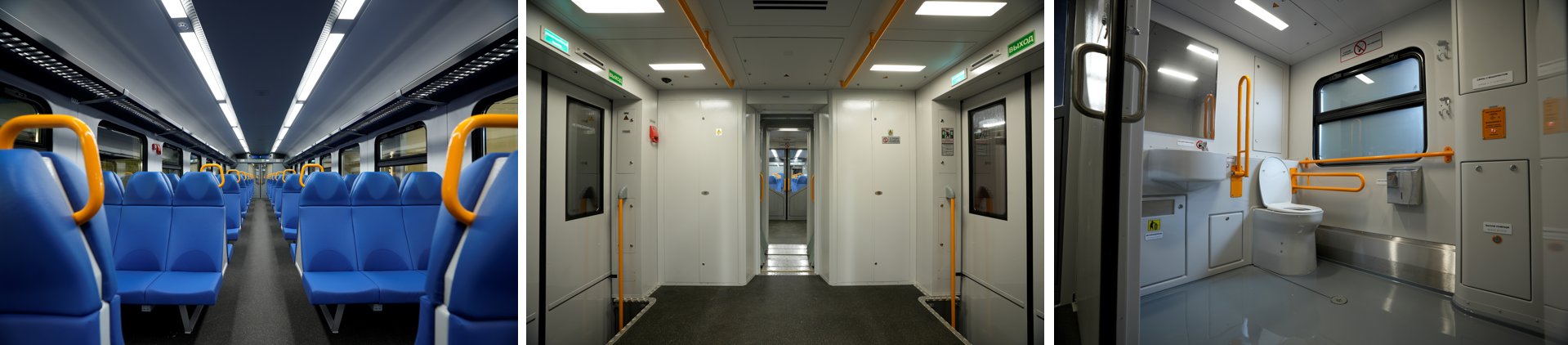 Interior of EP2DM train (enlarge). Source: TMH
Interior of EP2DM train (enlarge). Source: TMH
Currently, the EP2DM’s level of automation implies the control from driver and assistant. In the future, it is possible to upgrade the train to the GoA2 automation level.
The ergonomics of the passenger seats have been improved, the shape of the seat and back has been changed for more comfortable travel experience. The comfort was confirmed in tests carried out by passengers at one of the Moscow railway stations. The video surveillance system supplied by Transtelesoft (part of TMH Smart Systems) will now also monitor the dynamics of passenger traffic flow and the occupancy of cars.
 (enlarge)
(enlarge)
Developing DMZ: getting ready for more production
The Ministry of Transport of Russia highlighted the need to upgrade more than 6,000 regional train cars by 2030. Such target was mentioned in the draft concept for the development of regional railway transportation services in the country. TMH is realizing this potential need and is actively developing the production site in Demikhovo.
Nowadays, DMZ is capable of producing 630 new electric train cars per year. In 2022, the plant’s sales volume was the highest within 4 years. The customers received 429 new cars. These figures show that DMZ is the largest plant manufacturing electric trains among those located in Europe.
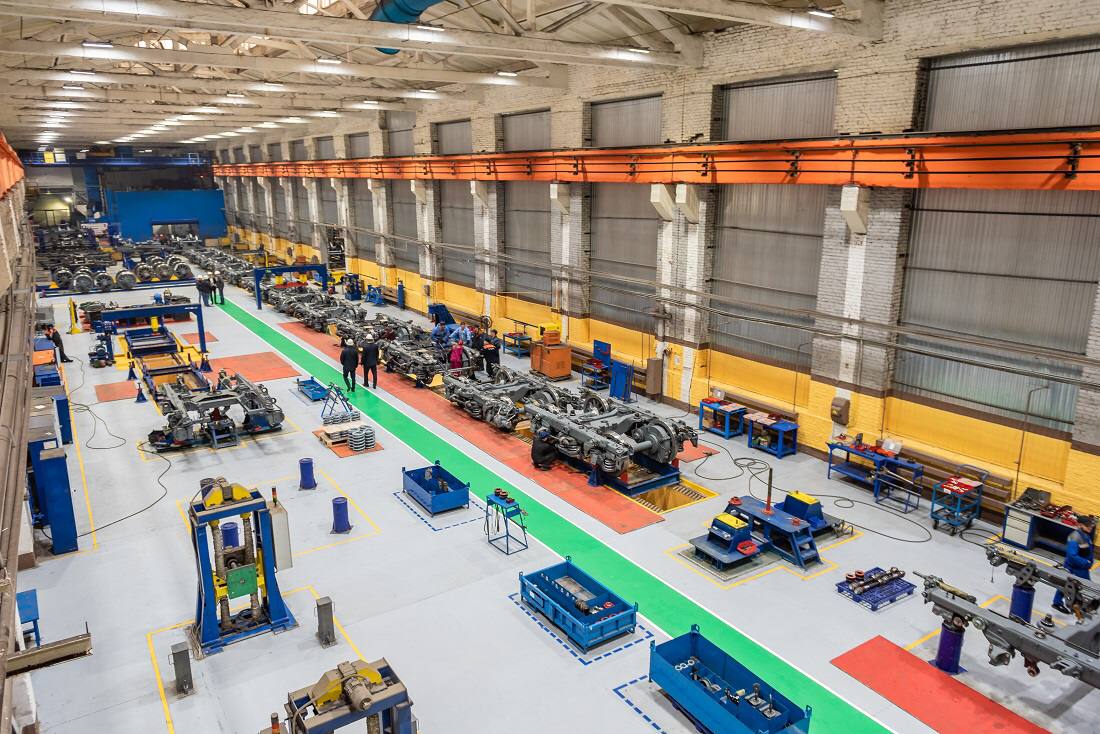 At the DMZ production site. Source: TMH
At the DMZ production site. Source: TMH
In the new economic conditions of 2022, DMZ also implemented the largest investment program for 4 years, amounting to 917 mln RUR ($10 mln). Within its framework, reference production flows were organized for the finishing stages of the electric trains production, the overhaul of ED4M cars and the assembly of motor bogies. A pre-fabricated module of the control and testing station for 2 additional positions was also built. It allowed to increase production capacity by 20% at once. At the car repair workshop, a gate opening for a through railway line was built. DMZ also upgraded 1,600 m2 of industrial and sanitary facilities. At the assembly site a new tilting stand was installed, which allows turning the bogie frame around the axis by 180° and fixing it in any intermediate position. As a result, the introduction of the control module for the reference assembly line allowed to control the bogies assembly online at the renovated area.
This year DMZ completed the construction of two electrified tracks with a total length of 760 m to test trains under voltage. The expansion of these capacities will reduce the waiting time for trials.
The plant is also optimizing storage facilities. Last spring, a new section was opened, providing parts for the welding production of electric trains. The first such project had previously been implemented to supply the reference assembly line.
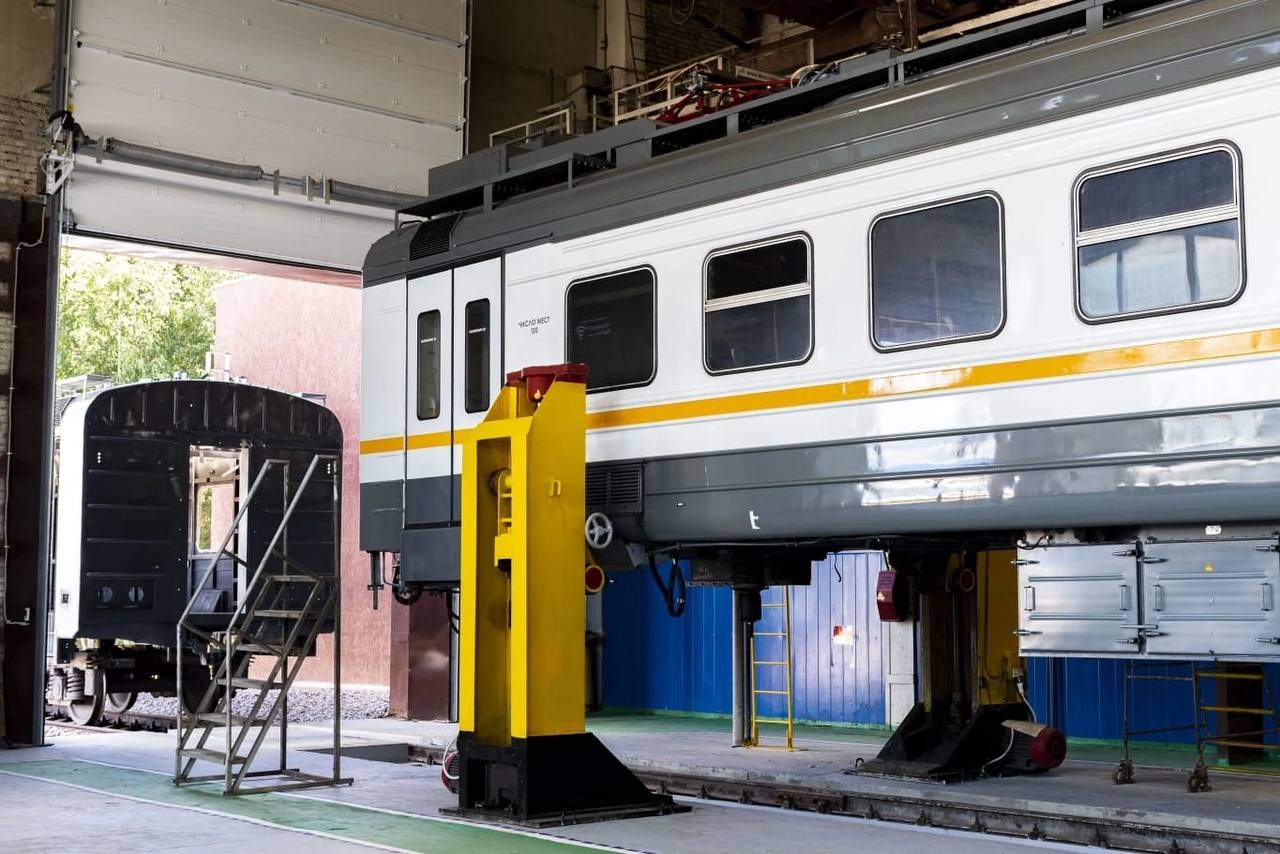 Gate opening for a through railway line at the DMZ car repair workshop. Source: TMH
Gate opening for a through railway line at the DMZ car repair workshop. Source: TMH
The digitalization of DMZ has been underway for almost 5 years, since October 2018. It is designed to make production and management more clear and efficient, as well as to improve product quality. One of the most important projects was the introduction of a system for intra-plant transport monitoring. A fleet of 51 vehicles was equipped with devices checking their condition and location. It helped to reduce fuel costs and improve production logistics. As part of the updated digital transformation strategy of TMH, 11 projects are planned to be implemented at the DMZ site. In particular, the introduction of digital enterprise simulation, online monitoring of production equipment operation, and other solutions are going to be applied.
The most important localization project at DMZ today is the development of the reduction drives production for railway multiple units and metro cars. It is being implemented with the support of the state Industrial Development Fund. A soft loan of 1.45 bln RUR ($16 mln) for the development of new competencies in the production of passenger transport was approved for DMZ in August last year. The project is of strategic importance for Russia. At the moment there isn’t any production of reduction drives in the country. Contracts for the supply of 11 units of production equipment have already been concluded. Now the deliveries are underway, as well as the necessary construction and installation work. According to the business plan, the production line should be put in operation at the beginning of 2024, allowing the manufacturing of up to 1200 reduction drives per year.
In total, DMZ plans to produce 528 new electric train cars in 2023, which is the one of the highest levels of production in its history. Today, the share of DMZ in the electric train production in Russia has grown to 75%. The rolling stock being manufactured by TMH is an example of work done for many years in the interests of Russia’s technological independence.
***

TMH is № 1 among railway and urban rail rolling stock manufacturers in Russia & CIS, № 5 in the world. The company offers a full range of products and services: from new rolling stock design and development to modernization, life cycle maintenance contracts and digital traffic control systems. TMH is a Russian company headquartered in Moscow with international subsidiaries in Egypt, Belarus and Kazakhstan. The holding structure includes 12 production and assembly sites in Russia and other countries worldwide. TMH supplies passenger trains and coaches, metro cars, locomotives, engines, and components to railway operators and manufacturers in 30 countries. Website: tmh.global
Advertising. Erid: 4CQwVszH9pUiLDd4Vpb















